Definition of "Muscle wasting"
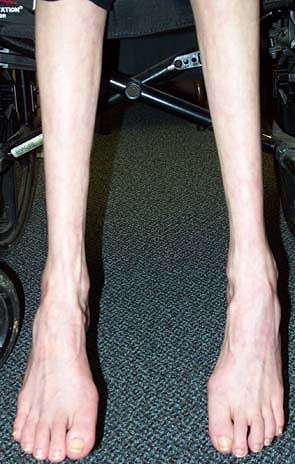
Muscle atrophy is a decrease in the mass of the muscle. It can be partial or complete wasting away of muscle, and is most commonly experienced when patients suffer temporary disabling circumstances, e.g. being restricted in movement and/or confined to bed as when hospitalized. When a muscle atrophies, it leads to muscle weakness, since the ability to exert force is related to mass. Muscle atrophy is a major factor behind the practice of getting hospitalized patients out of bed and moving about as active as possible as soon as feasible, despite sutures, wounds, broken bones, and pain. It results from a comorbidity of several common diseases, including cancer, AIDS, congestive heart failure, COPD, renal failure, and severe burns. Patients who have cachexia in disease settings have a poor prognosis. Moreover, starvation eventually leads to muscle atrophy. Disuse of the muscles, e.g. when muscle tissue is immobilized for even a few days of unuse, when the patient has a primary injury e.g. immobilized broken bone (set in a cast or immobilized in traction), for example, will also lead rapidly to disuse atrophy.
Source: WUSTL
Find a practitioner
Practitioner count: 0