Definition of "ECG"
Last modified: 22 hours
ECG (electrocardiography) is a record of electrical activity of the heart over time, detected by electrodes attached to the skin surface (non-invasive) at various set locations.
Method
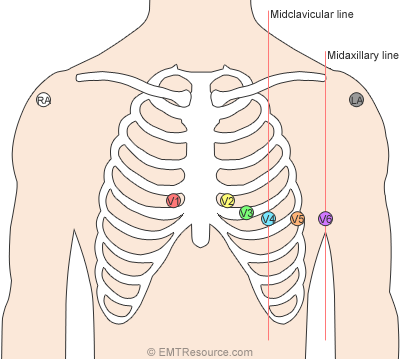
- The standard 12-lead ECG involves 10 electrodes, attached at RA (right arm), LA (left arm), RL (right leg), and LG (left leg). The other 6 are named from V1 to V6, with:
- V1 at the 4th intercostal right of sterum
- V2 at the 4th intercostal left of sterum
- V4 at the 5th intercostal in the mid-clavicular line
- V6 at the mid-axillary line
- V3 lies between V2 and V4
- V5 lies between V4 and V6
Source: 2014/04/12-lead-ecg-placement.png">EMT resource
Source: 2011/07/ECG-Anatomy-LITFL.jpg">Life in the fast lane
Interpretation
Source: Blogspot
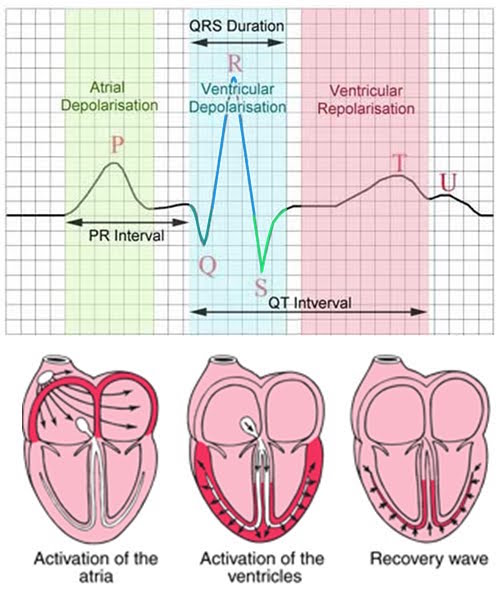
- P wave, is atrial depolarization, causing atrial contraction
- QRS complex, is depolarization of the R and L ventricles, causing ventricular contraction
- Q wave, is depolarization of the interventricular septum (i.e. wall separating the R and L ventricles)
- R wave, is depolarization of the R and L ventricular walls
- S wave, is depolarization of the Purkinje fibers
- T wave, is repolarization of the ventricles. The T wave is positive, even though REpolarization (i.e. the opposite of DEpolarization) is occurring, because of a double negative - REpolarization occurs in the OPPOSITE direction. However, aVR, is normally negative
Indications
Common patterns include:
- Rhythm:
- Sinus rhythm (SR), which is normal, having a regularly regular rhythm, and a HR of between 60-100bpm
- Sinus bradycardia, where the HR is <60bpm
- Sinus tachycardia, which is HR>100bpm. It is a tachycardia originating from the SA node
- Asystole, where the rhythm is flat, with no HR, no nothing. It is a state of no cardiac electrical activity, no contractions of the myocardium, no cardiac output or blood flow. It requires CPR
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), which is between 140-220bpm, with the P wave often buried in a preceding T wave. The PR interval depends on the location of the supraventricular pacemaker. It involves impulses stimulating the heart that aren't generated by the sinus/AV node [of the atria], but rather, come from tissue around or involving the AV node [of the ventricle]
- Atrial fibrillation, which is irregularly irregular, with a HR>100
- Atrial flutter, which has a regular rhythm, HR around 110bpm. P waves are around 300bpm, as they are replaced with multiple F (flutter) waves, at a ratio of 2:1 (F:QRS), or even 3:1
- Heart block (see page)
- Bundle branch block (BBB, see page)
- Premature ventricular complex, which involves an early QRS, to the point that it occurs simultaneously with the p-wave. it is caused by the ventricles depolarizing prematurely in response to a signal in the ventricles
- Junctional rhythms, where HR is between 40-60bpm, P wave is inverted in lead II. The SA node doesn't control the heart's rhythm, which can be caused by a block in conduction somewhere along the pathway. Rather, the heart's AV node takes over as the pacemaker
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT), where HR is 180-190bpm, QRS is prolonged, and P wave is not seen. It results from abnormal tissue in ventricles generating a rapid and irergular rhythm. It usually results in poor cardiac output, and thus cardiac arrest. If the Pt is unconscious and without a pulse, they will require shock
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF), where rhythm is irregular, HR is 300+ and disorganized, QRS is not recognizable, and P wave is not seen. It is caused by disorganized electrical signals causing the ventricles to quiver instead of contracting rhythmically. Condition may occur during or after MI. Pt is unconscious as blood isn't pumped into the brain. This Pt requires defibrillation quickly
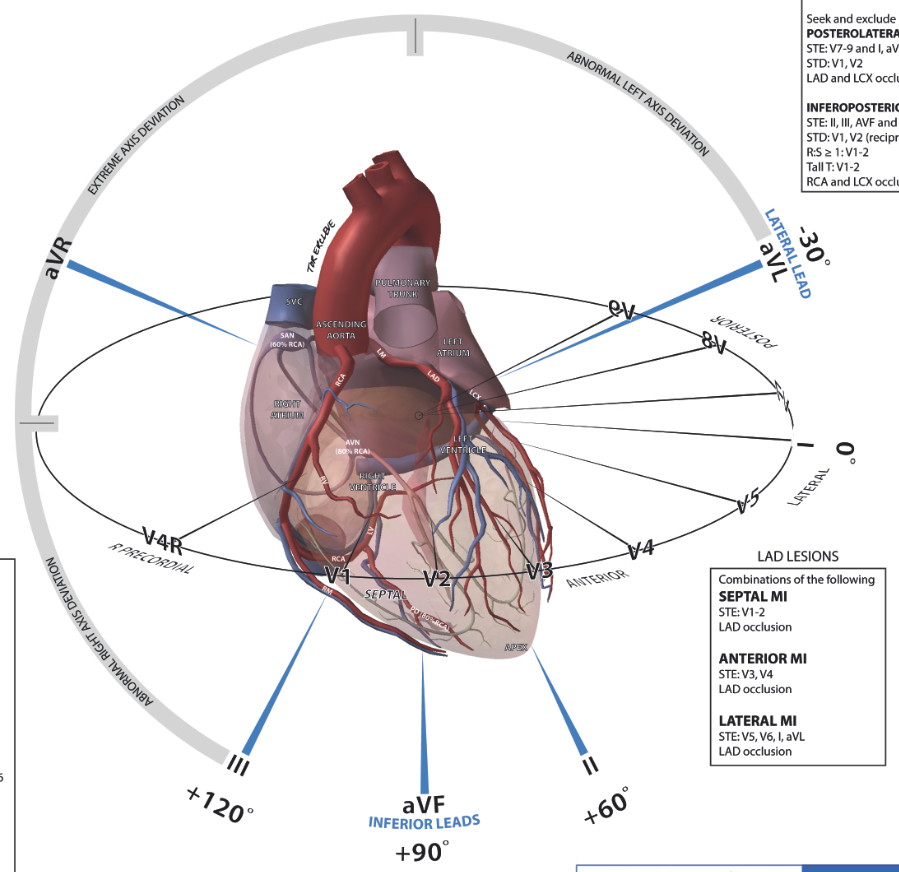
- Myocardial infarct (MI), where ST is not isoelectric (i.e. there is depression or elevation)
Source: Bioelectromagnetism
Paperwork
Paperwork for Electrocardiogram includes:
- Affix Pt label
- Data, including Requesting RMO sig, Date to be recorded, Date of previous ECG, Attended by, ECG serial No, Time recorded
- Section for Provisional Dx ___, Previous Medical Hx, IHD (Yes/No), M Infarction (Yes/No), Hypertension (Yes/No), Other, BP, Build
- Medications (cross out or daily dose), including YES/NO for Digitalis, Diuretics, Quinidine, Beta blockers, Tricyclics, Calcium antagonists, Other ___
- Report ____, and Reported by___
- Internal page has 4 vertical stickers, to permit the ECG to be stuck on
Paperwork for Request for diagnostic services:
- Affix Pt label
- Please tick the approprite box, tick for Inpatient, Outpatient
- Tick for Stress ECG, Trans-thoracic Echocardiogram, Trans-thoracic Echocardiogram with 3D study, Holter monitoring, Trans-esophageal echocardiogram, Stress echocardiogram (also tickbox for Exercise, Pharmacological), 12 Lead ECG (outpatients only)
- Pacemaker/defibrillator check, including tick for Guidant, Medtronic, Biotronik, St Jude, Other
- Clinical summary
- Indication for test
- ECG changes
- List of cardiac medications
- Authentication, including Requesting Dr name, Date, Requesting Dr signature, pager No, Requesting Dr provider number (for outpatients only)
See also
Synonyms:
Cardiac monitor
Cardiac monitoring
EKG
Electrocardiography
Heart monitor
Heart monitoring
P wave
Q wave
QRS
QRS complex
R wave
S wave
Sinus rhythm
SR
ST
T wave
Find a practitioner
Practitioner count: 0
Sponsor a disease. And see how your proceeds help.
$1
Express interest
$10
Write text
$40
Write FAQ
$100
Snap photos
$400
Record audio
$1k
Produce video
$4k
Interview experts