Definition of "Abdominal pain"
Abdominal pain (aka stomach pain) is pain in the abdomen. SNT is shorthand for soft non-tender.
- Undetermined cause (30%)
- Gastroenteritis (13%)
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) (8%)
- Urinary tract problems (5%)
- Gastritis (inflammation of the stomach) (5%)
- Constipation (5%)
- Gallbladder or pancreas problems (4%)
- Diverticulitis (3%)
- Appendicitis (2%)
- Cancer (1%)
- More common in the elderly, include:
- Mesenteric ischemia
- AAA (abdominal aorta aneurysms)
Patient information
What are the most common causes of tummy pain?So usually we don't know. Infection of the tummy and intestines. An irritable tummy system. Urinary tract problems, don't forget, because it's not necessarily the tummy system. Constipation is a biggy, particularly in kids. It can be the gallbladder, which stores bile, or the pancreas, which makes digestive enzymes. It can be inflammation of a diverticulum, which is an outpouching foudn in the large intestine. Appendicitis, which is inflammation of the appendix, which extends from the cecum, found just after ileocecal junction (i.e. junction of the ileum and cecum). It can be cancer. In the elderly, we also need to consider injury of the small intestine due to insufficient blood supply, or enlargement of the lower part of the major aorta artery.
- GI
- GI tract, including:
- Inflammatory: gastroenteritis, appendicitis, gastritis, esophagitis, diverticulitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, microscopic colitis
- Obstruction: hernia, intussusception, volvulus, post-surgical adhesions, tumors, superior mesenteric artery syndrome, severe constipation, hemorrhoids
- Vascular: embolism, thrombosis, hemorrhage, sickle cell disease, abdominal angina, blood vessel compression (e.g. celiac artery compression syndrome), postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
- Digestive: peptic ulcer, lactose intolerance, celiac disease, food allergies
- Glands:
- Bile system:
- Inflammatory: cholecystitis, cholangitis
- Obstruction: cholelithiasis, tumors
- Liver:
- Inflammatory hepatitis, liver abscess
- Pancreatic:
- Inflammatory: pancreatitis
- Bile system:
- GI tract, including:
- Renal and urological:
- Inflammation: pyelonephritis, bladder infection
- Obstruction: kidney stones, urolithiasis, urinary retention, tumors
- Vascular: L renal vein entrapment
- Gynecological or obstetric:
- Inflammatory: PID (pelvic inflammatory disease)
- Mechanical: ovarian torsion
- Endocrinological: menstruation, Mittelschmerz
- Tumors: endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian cyst, ovarian cancer
- Pregnancy: ruptured ectopic pregnancy, threatened abortion
- Abdominal wall:
- Muscle strain or trauma
- Muscular infection
- Neurogenic pain: herpes zoster, radiculitis in Lyme disease, abdominal cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES), tabes dorsalis
- Referred pain:
- From the thorax: pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, ischemic heart disease, pericarditis
- From the spine: radiculitis
- From the genitals: testicular torsion
- Metabolic disturbance:
- Uremia, diabetic ketoacidosis, porphyria, C1-esterase inhibitor deficiency, adrenal insufficiency, lead poisoning, black widow spider bite, narcotic withdrawal
- Blood vessels:
- Aortic dissection, AAA (abdominal aortic aneurysm)
- Immune system:
- Sarcoidosis
- Vasculitis
- Familial Mediterranean fever
- Idiopathic:
- Irritable bowel syndrome, affecting up to 20% of the population, IBS is the most common cause of recurrent, intermittent abdominal pain
Patient information
What can cause pain in the tummy?The most obvious one, is something relating to your eating system, which also includes your liver, which helps clean blood, and also makes bile. The pancreas, which makes digestive enzymes. And the bile system, which transports and stores bile. It can also be your kidneys, although they're a little off to the sides. Women's reproductive system, don't forget. Musculoskeletal type pain. The aorta blood vessel, which is also found in the region. It can also be referred from a further distance, like the chest, the spine, or testicles.
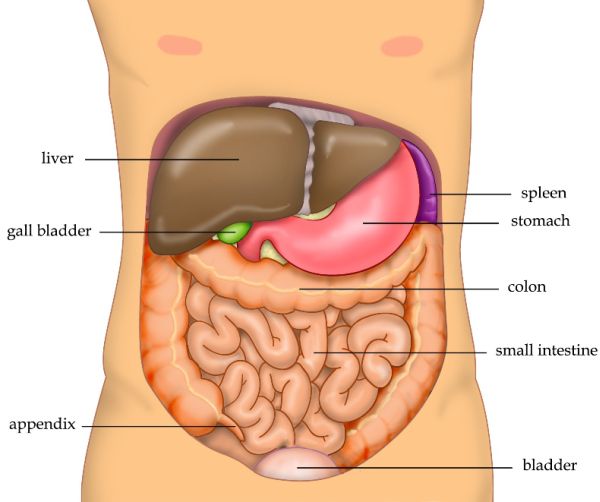
Source: Wikimedia
- Upper RHS (hypochondric), can be:
- Liver: hepatomegaly, caused by fatty liver, hepatitis, liver cancer, abscess
- Gallbladder and biliary tract: gallstones, inflammation
- Colon: bowel obstruction, colon cancer
- Upper middle (epigastric), can be:
- Stomach: gastritis, stomach ulcer, stomach cancer
- Pancreas: pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, which can radiate to the LHS
- Duodenum: duodenal ulcer, diverticulitis
- Appendix: appendicitis, which migrates to the lower RHS
- Upper LHS (hypochondric), can be:
- Spleen: splenomegaly
- Pancreas
- Colon: bowel obstruction, colon cancer
- Middle (umbilical; or if towards the sides, lumbar; or if lower, hypogastric), can be:
- Appendix: appendicitis
- Small intestine: inflammation
- Lower RHS (iliac), can be:
- Cecum: intussusception, bowel obstruction
- Appendix: appendicitis
- Lower middle:
- Diarrhea
- Colitis
- Dysentery
- Lower LHS (iliac), can be:
- Sigmoid colon: polyps, volvulus, obstruction
- Pelvic pain:
- Bladder: cystitis (may be secondary to diverticulum), bladder stone, bladder cancer
- Pain in women: uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes
- Lower back pain:
- Kidney pain: kidney stone, kidney cancer, hydronephrosis
- Ureteral stone pain
- R lower back pain:
- Liver pain (hepatomegaly)
- R kidney pain
- L lower back pain:
- Less in spleen pain
- L kidney pain
Patient information
You can also classify a tummy ache, based on location?Yep, so we like to divide the tummy into 9 areas, using lines drawn like noughts and crosses. On the upper RHS, there's the liver, gallbladder which stores bile, and the bile system. In the middle upper, there's the tummy, the pancreas which lies behind the tummy, the duodenum which is the 1st part of the small intestine. The upper LHS, where there is the spleen, just to the right of the tummy and liver. The pancreas, as it lies behind the tummy, also extends to the RHS. In the middle at the belly button, there's the small intestine, it's a bit like a swirl so the small intestine is central, and the large intestine is towards the outer edges. The lower RHS has the appendix and the cecum, which is the 1st part of the large intestine. The lower middle is the large intestine, so it can be diarrhea, or inflammation of the large intestine. The lower LHS is the sigmoid part of the large intestine, which is the S shaped part that is found just before the rectum.
That's quite a big mouthful. But there's also a few other side locations?
Yep, so pelvic pain, can be the bladder, or women's reproductive tract. There's also lower back pain, it can be a urinary tract stone, or kidney pain, which can also be towards the side. If it's towards the right back, it can be the liver, or if in the left back it can be the spleen, although recall that it's found at the front on the upper RHS.
Acute abdomen is sudden, severe abdominal pain of unclear etiology, <24 hours in duration. It is in many cases a medical emergency, with several causes requiring surgical Tx. Causes include:
- Traumatic:
- Blunt or perforating trauma to the stomach, bowel, spleen, liver, or kidney
- Inflammatory:
- Infections, including:
- Acute appendicitis, most commonly
- Acute cholecystitis
- Acute diverticulitis
- Acute pancreatitis
- Acute peritonitis
- Acute pyelonephritis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Hepatitis
- Mesenteric adenitis
- Subdiaphragmatic abscess
- Perforation of:
- Acute peptic ulcer
- Diverticulum
- Cecum
- Complications of inflammatory bowel diseases, including:
- Crohn's disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Infections, including:
- Mechanical:
- Small bowel obstruction, secondary to:
- Adhesions caused by previous surgeries
- Intussusception
- Hernias
- Benign or malignant neoplasms
- Large bowel obstructions, caused by:
- Colorectal cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Bowel volvulus
- Fecal impaction
- Hernia
- Small bowel obstruction, secondary to:
- Vascular:
- Acute occlusive intestinal ischemia, usually caused by thromboembolism of the SMA (superior mesenteric artery)
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Hemoperitoneum
- Sickle cell anemia
- Other:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Ovarian torsion
- Acute uteric colic
- Adrenal crisis
- Biliary colic
- Ruptured spleen
- Kidney stone
- Pain relief
- Common Sx
- Determinig the cause can be diffcult, because many diseases can cause the Sx
Find a practitioner
Practitioner count: 0